# - For note making in the program,
the sentence after # would not be a part of the program while running.
The Rules in Naming Variables:
Variables names must start with a letter or an underscore, such as:
- _underscore (O)
- underscore_ (O)
- under-score (X)
The remainder of your variable name may consist of letters, numbers and underscores.
- password1 (O)
- n00b (O)
- un_der_scores (O)
- 1password (X)
Names are case sensitive.
- case_sensitive, CASE_SENSITIVE, and Case_Sensitive are each a different variable.
Reserved words can not be named as other variables
Here’s a list of reserved words but not all included:

- b = 5566 (O)
- break = 5566 (X)
Types of literal:
- string e.g. agenda, python5566
- bytes
- integer e.g. 5566
- floating-point e.g. 5.566
- imaginary
Types of data:
- int e.g. 5566
- float e.g. 5.566
- complex e.g. 556+6j
- str e.g. python5566
- bytes
- bytearray
- list e.g. [1,2,3,4,5], [1,2,(3),[4,5]]
- tuple e.g. (1,2,3,4,5), (1,2,(3),[4,5])
- set e.g. {1,2,3,4,5} == {1,1,1,1,1,2,3,4,5,5}
- dict {key:value} e.g. {1:abba, 2:Bb}
Sub-functions used in ‘list’ data:
| Operation | Result | Notes |
|---|---|---|
s[i] = x |
item i of s is replaced by x | |
s[i:j] = t |
slice of s from i to j is replaced by the contents of the iterable t | |
del s[i:j] |
same as s[i:j] = [] |
|
s[i:j:k] = t |
the elements of s[i:j:k] are replaced by those of t |
(1) |
del s[i:j:k] |
removes the elements of s[i:j:k] from the list |
|
s.append(x) |
appends x to the end of the sequence (same ass[len(s):len(s)] = [x]) |
|
s.clear() |
removes all items from s (same as del s[:]) |
(5) |
s.copy() |
creates a shallow copy of s (same as s[:]) |
(5) |
s.extend(t) or s += t |
extends s with the contents of t (for the most part the same as s[len(s):len(s)] = t) |
|
s *= n |
updates s with its contents repeated n times | (6) |
s.insert(i, x) |
inserts x into s at the index given by i (same as s[i:i]= [x]) |
|
s.pop([i]) |
retrieves the item at i and also removes it from s | (2) |
s.remove(x) |
remove the first item from s where s[i] == x |
(3) |
s.reverse() |
reverses the items of s in place | (4) |
Functions used in ‘set’ data:
| Operation | Result | Notes |
|---|---|---|
x | y |
bitwise or of x and y | |
x ^ y |
bitwise exclusive or of x and y | |
x & y |
bitwise and of x and y | |
x << n |
x shifted left by n bits | (1)(2) |
x >> n |
x shifted right by n bits | (1)(3) |
~x |
the bits of x inverted |
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| s1.intersection(s2) | 等於 s1 & s2 |
| s1.union(s2) | 等於 s1 | s2 |
| s1.symmetric_difference(s2) | 等於 s1 ^ s2 |
| s1.difference(s2) | 等於 s1 – s2 |
| s1.issubset(s2) | 等於 s1 <= s2 |
| s1.issuperset(s2) | 等於 s1 >= s2 |
| s1.isdisjoint(s2) | 判斷 s1 與 s2 是否無交集,若無交集,回傳 True |
| s.copy() | 回傳 s 的拷貝 |
由於 set 型態是可變的,因此有額外兩個新增與刪除元素的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| s.add(e) | 增加 e 為 s 的元素 |
| s.remove(e) | 從 s 中刪除元素 e |
For ‘dict’ data:
| 計算 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| d[key] | 從 d 中取得 key 的 value |
| d[key] = value | 將 d 的 key 指定為 value |
| del d[key] | 刪除 d 中 key 所指定的 value |
| key in d | 判斷 key 是否在 d 中 |
| key not in d | 判斷 key 是否不在 d 中 |
| iter(d) | 回傳由 d 的 key 建立的迭代器 |
| len(d) | 回傳 d 的配對資料個數 |
字典物件有以下的方法 (method)
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| dict.clear() | 清空 dict 的所有配對資料 |
| dict.copy() | 回傳 dict 的拷貝 |
| classmethod dict.fromkeys(seq[, value]) | 由 seq 中的元素構成 key ,每個 key 都給相同的 value 值 |
| dict.get(key[, default]) | 從 dict 中取得 key 的 value ,若無此 key 則回傳 default , default 預設為 None |
| dict.items() | 回傳 dict_items 物件,使 key:value 儲存為序對,然後依序儲存在 dict_items 物件中 |
| dict.keys() | 回傳 dict_items 物件,使 key 依序儲存在 dict_items 物件中 |
| dict.pop(key[, default]) | 將 key 的 value 從 dict 移除,若無此 kay ,回傳 default |
| dict.popitem() | 從 dict 移除任意一組 key:value |
| dict.setdefault(key[, default]) | 如果 key 在 dict 中,回傳 value 值,反之,將 key:default 加入 dict 之中 |
| dict.update([other]) | 將 dict 以 other 更新 |
| dict.values() | 回傳 dict_items 物件,使 value 依序儲存在 dict_items 物件中 |
----
Exercise 1:
Solve the questions listed below with data type “set":
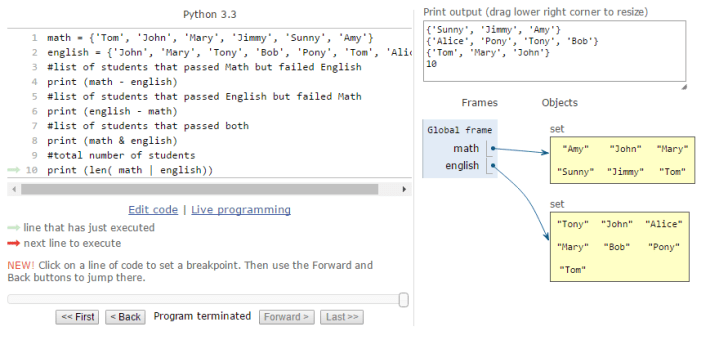
List of students who have passed the final Math exam in the class: Tom, John, Mary, Jimmy, Sunny, Amy;
List of students who have passed the final English exam in the class: John, Mary , Tony , Bob , Pony, Tom , Alice
- print the list of students that passed Math but failed English;
- print the list of students that passed English but failed Math;
- print the list of students that passed both; finally
- print the total number of students.
Exercise 2:
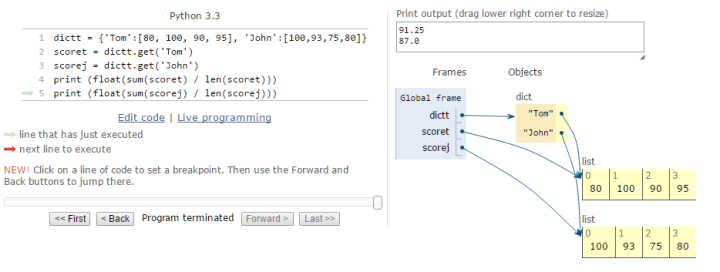
Solve the questions listed below with data type “dict" and “list":
Scores of Tom: 80, 100, 90, 95
Scores of John: 100,93,75,80
Store the data with data type ‘dict’ and print the average score of each.
--
Next: Loops and If functions
--
Reference:
Coursera
PPT from NTU SPECS course